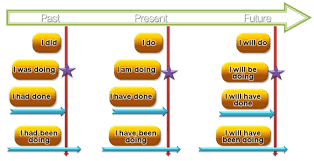
Tenses ในภาษาอังกฤษ มีทั้งหมด 3 ประเภท ประเภทละ 4 ชนิด ดังนี้
I. Present Tenses
1. Present Simple Tense
2. Present Continuous Tense
3. Present Perfect Tense
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
II. Past Tenses
1. Past Simple Tense
2. Past Continuous Tense
3. Past Perfect Tense
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
III. Future Tenses
1. Future Simple Tense
2. Future Continuous Tense
3. Future Perfect Tense
4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
I.
1. Present Simple Tense
(ปัจจุบันกาลปกติ)
โครงสร้าง : Subject + Verb 1
(ปัจจุบันกาลปกติ)
โครงสร้าง : Subject + Verb 1
1)ใช้พูดถึงเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ เกิดขึ้นอยู่ตลอดเวลา หรือ เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำซ้ำไปซ้ำมา เช่น
I drink a lot of water. (ฉันดื่มน้ำเยอะ)
2)ใช้
กับการกระทำที่ ทำจนเป็นอุปนิสัย หรือ ใช้เพื่อแสดงความถี่ของการกระทำต่างๆ
โดยเรามักใช้กับ คำกริยาวิเศษณ์แสดงความถี่ (Adverbs of Frequency)
มาช่วยในการแสดงความถี่ของการกระทำ เช่น
I always do my homework. (ฉันทำการบ้านของฉันเสมอ)
Snow is white. (หิมะมีสีขาว)
4)ใช้เมื่อต้องการพูดถึง ตารางเวลา (Schedule) หรือ แผนการ (Plan) ที่ได้วางไว้ เช่น
The meeting starts from 8.30 am until 10.00 pm.
(การประชุมเริ่มตอนแปดโมงครึ่งตอนเช้าไปยังสี่ทุ่ม)
5)ใช้ในการ แนะนำ บอกแนวทาง หรือ สอน เช่น
How do I get to the nearest mall? Go straight and turn left on the next corner.
(ฉันจะไปยังห้างที่ใกล้ที่สุดได้อย่างไร เดินตรงไปแล้วเลี้ยวซ้ายตรงหัวมุมข้างหน้า
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Present Simple Tense
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +is/am/are + V -ing
1) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ เกิดขึ้นในอดีต และดำเนินต่อเนื่องมายังปัจจุบัน และมีแนวโน้น
ที่จะดำเนินต่อไปได้อีกในอนาคต เช่น
2) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ เกิดขึ้นและสิ้นสุดลงแล้ว แต่ยังส่งผลมายังปัจจุบัน เช่น
3)ใช้ พูดถึง เหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำๆกัน ในช่วงเวลาหนึ่งระหว่างอดีตและปัจจุบัน
โดยมักใช้คำว่า many/several times, a lot of times, …times, again and again,
over and over และอื่นๆ เช่น
4)ใช้ กับเหตุการณ์ที่ เพิ่งสิ้นสุดลง โดยไม่ระบุเวลา ซึ่งมักใช้กับ just, already และ yet yet มักใช้ในประโยคปฏิเสธ ส่วน just และ already นั้น มักจะใช้กันในประโยคบอกเล่า โดยวางไว้อยู่หน้ากริยาหลัก
เช่น
5)ใช้เพื่อบอกเล่าถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เพิ่งเกิดขึ้นเร็วๆ นี้ ซึ่งมักใช้กับ just, recently, lately และอื่นๆ
1)คำ กริยาที่ใช้กับ Present Perfect Continuous Tense นั้น จะต้องเป็นคำกริยา
ที่แสดงถึงความต่อเนื่อง หรือ กริยาที่แสดงถึงการกระทำที่นาน (long action) เท่านั้น
เช่น play, look, watch, learn, live, wait, eat และอื่นๆ โดยไม่สามารถใช้กับกริยา
ที่ไม่แสดงถึงความต่อเนื่อง หรือ กริยาที่แสดงถึงการกระทำที่จบในทันทีได้ เช่น
stop, prefer, arrive เป็นต้น เช่น
2)ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ เกิดขึ้นในอดีตต่อเนื่องมายังปัจจุบัน และยังคงดำเนินต่อไปอีก
ในอนาคต โดยใช้กับคำว่า since และ for เช่น
3) Present Perfect Continuous Tense อาจนำมาใช้ได้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ สิ้นสุดลงแล้ว
แต่ส่งผลมายังปัจจุบัน เช่น
4) Present Perfect Continuous Tense จะ เน้นถึงความต่อเนื่องของการกระทำ
(Continuity of action) มากกว่า Present Perfect Tense
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Present Perfect Continuous Tense

*เราใช้ “did” เข้ามาช่วยในการสร้างประโยคคำถามหรือปฏิเสธ โดยกริยาแท้นั้นจะต้องอยู่ในรูปกริยาช่องที่ 1 เท่านั้น
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ did not คือ didn’t
2. Past Continuous Tense (อดีตกาลต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +was/were + V -ing


3. Past Perfect Tense
(อดีตกาลสมบูรณ์)
โครงสร้าง : Subject +had + V 3
1)ใช้ กับเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ ที่ เกิดขึ้น และสิ้นสุดลงแล้วในอดีตทั้ง 2 เหตุการณ์ ซึ่งเหตุการณ์หนึ่งได้สิ้นสุดลงก่อนหน้าอีกเหตุการณ์ โดย…
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นและสิ้นสุดลงก่อน จะใช้ Past Perfect Tense
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นและสิ้นสุดลงทีหลัง จะใช้ Past Simple Tense เช่น
2) Past Perfect Tense มักจะใช้กับคำว่า before, after, already, just, yet, until, till, as soon as, when, by the time, by… (เช่น by this month) และอื่นๆ โดยจะมีอาจวิธีการใช้ต่างกันไป เช่น
Before + Past Simple Tense + Past Perfect Tense :
After + Past Perfect Tense + Past Simple Tense :
By he time + Past Simple Tense + Past Perfect Tense :
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
1) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ เกิดขึ้นและดำเนินต่อเนื่องมาจนถึงอีกเหตุการณ์หนึ่งในอดีต โดยอาจใช้กับคำว่า since และ for เช่น
2) ใช้พูดถึงการกระทำที่ เกิดขึ้นซ้ำไปซ้ำมาในอดีต และได้สิ้นสุดลงแล้ว เช่น
3) Past Perfect Continuous Tense จะเน้นถึงความต่อเนื่องของการกระทำ (Continuity of action) มากกว่า Past Perfect Tense
That man had been eating pizza when I came in.
1. Future Simple Tense (อนาคตกาลปกติ)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject + will + Verb 1
2. Future Continuous Tense
(อนาคตกาลต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +will + be + V-ing


3. Future Perfect Tense
(อนาคตกาลสมบูรณ์)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject + will + have +V3
1) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ คาดว่าจะสิ้นสุดในช่วงเวลาที่กำหนดไว้
4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense (อนาคตกาลสมบูรณ์ต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :

และภาพประกอบจาก www.google.com
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + Verb1
| |||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
I / You / We / They
|
eat
|
seafood.
| |||||||
He / She / It
|
knows
|
about you.
| ||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + do/does + not + Verb1
| |||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
I / You / We / They
|
do
|
not
|
eat
|
seafood.
| |||||
He / She / It
|
does
|
not
|
know
|
about you.
| ||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Do/Does + Subject + Verb1?
| |||||||||
คำถาม
|
Do
|
I / you / we / they
|
eat
|
seafood?
| ||||||
Does
|
he / she / it
|
know
|
about you?
| |||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + do/does + Subject +Verb1?
| |||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
Why
|
do
|
I / you / we / they
|
eat
|
seafood?
| |||||
What
|
does
|
he / she / it
|
know
|
about you?
| ||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ do/does not คือ don’t และ doesn’t
2. Present Continuous Tense
(ปัจจุบันกาลต่อเนื่อง)
(ปัจจุบันกาลต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +is/am/are + V -ing
1)ใช้
กับเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ กำลังดำเนินอยู่ในขณะที่พูด
ต่อเนื่องไปเรื่อยๆ
และจบในอนาคต โดยอาจจะใช้ Adverbs of Time (คำกริยาวิเศษณ์บอกเวลา) บางคำ
เช่น now, at the moment, right now, at present, these days เป็นต้น
เข้ามาช่วยในประโยคด้วย เช่น
และจบในอนาคต โดยอาจจะใช้ Adverbs of Time (คำกริยาวิเศษณ์บอกเวลา) บางคำ
เช่น now, at the moment, right now, at present, these days เป็นต้น
เข้ามาช่วยในประโยคด้วย เช่น
She is going to the supermarket at the moment.
(หล่อนกำลังไปซุปเปอร์มาร์เกตอยู่ตอนนี้)
2)ใช้เพื่อพูดถึงเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ กำลังจะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตอันใกล้ เช่น
I am meeting my boss this evening.
(ฉันจะพบกับเจ้านายเย็นนี้)
3)ใช้แสดงเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ ผู้พูดมั่นใจว่าจะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตอย่างแน่นอน เช่น
He is going to China tonight.
(เขาจะเดินทางไปยังประเทศจีนคืนนี้)
4)กริยา
บางตัวไม่สามารถใช้ในรูปของ Present Continuous Tense ได้
ถึงแม้ว่าเหตุการณ์นั้นจะกำลังเกิดขึ้น หรือ ดำเนินอยู่ก็ตาม โดยเรามักใช้ในรูปของ
Present Simple Tense กับคำกริยากลุ่มนี้แทน ซึ่ง ได้แก่
ถึงแม้ว่าเหตุการณ์นั้นจะกำลังเกิดขึ้น หรือ ดำเนินอยู่ก็ตาม โดยเรามักใช้ในรูปของ
Present Simple Tense กับคำกริยากลุ่มนี้แทน ซึ่ง ได้แก่
4.1) กริยาที่แสดงถึงประสาทสัมผัสทั้งห้า เช่น see, hear, feel, taste, smell
I smell something bad. (ถูก)
I am smelling something bad. (ผิด)
4.2)
กริยาที่แสดงความนึกคิด ความรู้สึก เช่น know, understand, think,
believe, agree, notice, doubt, suppose, forget, remember, consider, recognize,
appreciate, forgive
believe, agree, notice, doubt, suppose, forget, remember, consider, recognize,
appreciate, forgive
I believe her. (ถูก)
I am believing her. (ผิด)
4.3) กริยาที่แสดงความชอบและความไม่ชอบ เช่น like, dislike, love,
hate, prefer, trust, detest
hate, prefer, trust, detest
He likes a woman with long hair. (ถูก)
He is liking a woman with long hair. (ผิด)
4.4) กริยาที่แสดงความปรารถนา เช่น wish, want, desire, prefer
I want to get married. (ถูก)
I am wanting to get married. (ผิด)
4.5) กริยาที่แสดงความเป็นเจ้าของ เช่น possess, have, own, belong
She has no children. (ถูก)
She is having no children. (ผิด)
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Present Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + is/am/are + V.-ing
| |||||||
บอกเล่า
|
I | am | talking | to her. | ||||
| You / We / They | are | reading | magazines. | |||||
| He / She / It | is | sleeping | on the couch. | |||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + is/am/are + not + V.-ing
| |||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
I | am | not | talking | to her. | |||
| You / We / They | are | not | reading | magazines. | ||||
| He / She / It | is | not | sleeping | on the couch. | ||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Is/Am/Are + Subject + V.-ing?
| |||||||
คำถาม
|
Am | I | talking | to her? | ||||
| Are | you / we / they | reading | magazines? | |||||
| Is | he / she / it | sleeping | on the couch? | |||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + is/am/are + Subject + V.-ing?
| |||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
Who
|
am | I | talking to? | ||||
What
|
are | you / we / they | reading? | |||||
Where
|
is | he / she / it | sleeping? | |||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ is / am / are not คือ isn’t, aren’t และ aren’t
3. Present Perfect Tense
(ปัจจุบันกาลสมบูรณ์)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +has/have + V3
(ปัจจุบันกาลสมบูรณ์)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +has/have + V3
1) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ เกิดขึ้นในอดีต และดำเนินต่อเนื่องมายังปัจจุบัน และมีแนวโน้น
ที่จะดำเนินต่อไปได้อีกในอนาคต เช่น
I have had a lot of toys.
ฉันมีของเล่นมากมาย (และอาจจะมีของเล่นเพิ่มขึ้นอีกในอนาคต)
2) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ในอดีตที่ เกิดขึ้นและสิ้นสุดลงแล้ว แต่ยังส่งผลมายังปัจจุบัน เช่น
It has stopped raining.
ฝนหยุดตกแล้ว (แต่ถนนยังเปียกอยู่)
3)ใช้ พูดถึง เหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำๆกัน ในช่วงเวลาหนึ่งระหว่างอดีตและปัจจุบัน
โดยมักใช้คำว่า many/several times, a lot of times, …times, again and again,
over and over และอื่นๆ เช่น
I’ve read this book more than 3 times.
(ฉันอ่านหนังสือเล่มนี้มามากกว่าสามรอบแล้ว)
4)ใช้ กับเหตุการณ์ที่ เพิ่งสิ้นสุดลง โดยไม่ระบุเวลา ซึ่งมักใช้กับ just, already และ yet yet มักใช้ในประโยคปฏิเสธ ส่วน just และ already นั้น มักจะใช้กันในประโยคบอกเล่า โดยวางไว้อยู่หน้ากริยาหลัก
เช่น
I haven’t finished my homework yet.
(ฉันยังทำการบ้านของฉันไม่เสร็จเลย)
5)ใช้เพื่อบอกเล่าถึงเหตุการณ์ที่เพิ่งเกิดขึ้นเร็วๆ นี้ ซึ่งมักใช้กับ just, recently, lately และอื่นๆ
The meeting has just started.
(การประชุมเพิ่งจะเริ่มขึ้น)
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Present Perfect Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + has/have + Verb 3
| |||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
I / You / We / They | have | talked | to her. | ||||||
| He / She / It | has | slept | on the couch. | |||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + has/have + not + Verb 3
| |||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
I / You / We / They | have | not | talked | to her. | |||||
| He / She / It | has | not | slept | on the couch. | ||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Has/Have + Subject + Verb 3?
| |||||||||
คำถาม
|
Have | I / you / we / they | talked | to her? | ||||||
| Has | he / she / it | slept | on the couch? | |||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + has/have + Verb 3?
| |||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
Who
|
have | I / you / we / they | talked to? | ||||||
Where
|
has | he / she / it | slept? | |||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ has/have not คือ hasn’t และ haven’t
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
(ปัจจุบันกาลสมบูรณ์ต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +has/have +been + V -ing
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +has/have +been + V -ing
1)คำ กริยาที่ใช้กับ Present Perfect Continuous Tense นั้น จะต้องเป็นคำกริยา
ที่แสดงถึงความต่อเนื่อง หรือ กริยาที่แสดงถึงการกระทำที่นาน (long action) เท่านั้น
เช่น play, look, watch, learn, live, wait, eat และอื่นๆ โดยไม่สามารถใช้กับกริยา
ที่ไม่แสดงถึงความต่อเนื่อง หรือ กริยาที่แสดงถึงการกระทำที่จบในทันทีได้ เช่น
stop, prefer, arrive เป็นต้น เช่น
I have been playing games since afternoon.
(ฉันเล่นเกมส์มาตั้งแต่ตอนบ่าย)
2)ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ เกิดขึ้นในอดีตต่อเนื่องมายังปัจจุบัน และยังคงดำเนินต่อไปอีก
ในอนาคต โดยใช้กับคำว่า since และ for เช่น
She has been sitting here for an hour.
(เธอนั่งอยู่ตรงนี้มาเป็นเวลาชั่วโมงหนึ่งแล้ว)
3) Present Perfect Continuous Tense อาจนำมาใช้ได้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ สิ้นสุดลงแล้ว
แต่ส่งผลมายังปัจจุบัน เช่น
You look tired. Have you been sleeping properly?
(คุณดูเหนื่อยจัง คุณได้นอนหลับมาเพียงพอหรือเปล่า)
4) Present Perfect Continuous Tense จะ เน้นถึงความต่อเนื่องของการกระทำ
(Continuity of action) มากกว่า Present Perfect Tense
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Present Perfect Continuous Tense 
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + has/have + been + V.-ing
| ||||||||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
I / You / We / They | have | been | working | in the office. | ||||||||||
| He / She / It | has | been | watching | the television. | |||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + has/have + not + been + V.-ing
| ||||||||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
I / You / We / They | have | not | been | working | in the office. | |||||||||
| He / She / It | has | not | been | watching | the television. | ||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Has/Have + Subject + been + V.-ing?
| ||||||||||||||
คำถาม
|
Have | I / you / we / they | been | working | in the office? | ||||||||||
| Has | he / she / it | been | watching | the television? | |||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + has/have + Subject + been + V.-ing?
| ||||||||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
Who
|
have | I / you / we / they | been | talking to? | ||||||||||
Where
|
has | he / she / it | been | sleeping? | |||||||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ has/have not คือ hasn’t และ haven’t
II.
1. Past Simple Tense (อดีตกาลปกติ)
โครงสร้าง : Subject + Verb ช่อง 2
โครงสร้าง : Subject + Verb ช่อง 2
1)
ใช้กับเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ เกิดขึ้นในอดีตและสิ้นสุดลงแล้ว
ซึ่งมักจะมีคำ
หรือวลีที่บ่งบอกถึงเวลาในอดีตในประโยคเสมอ เช่น yesterday, last…, … ago,
once, this morning, when I was… และอื่นๆ เช่น
หรือวลีที่บ่งบอกถึงเวลาในอดีตในประโยคเสมอ เช่น yesterday, last…, … ago,
once, this morning, when I was… และอื่นๆ เช่น
I met a beautiful girl last night.
(ฉันเจอผู้หญิงสวยคนหนึ่งเมื่อคืนนี้)
2)
ใช้แสดงถึงการกระทำที่เป็นนิสัยหรือเกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำในอดีต
ซึ่งสิ้นสุดลงแล้ว
โดยมักมี Adverbs of Frequency (กริยาวิเศษณ์แสดงความถี่) อยู่ในประโยคด้วย
เช่น often, always, sometimes และอื่นๆ ซึ่งมักจะมี Adverb of Time
(กริยาวิเศษณ์แสดงเวลา) ระบุถึงเวลาในอดีตด้วย เช่น last month, last year และอื่นๆ เช่น
โดยมักมี Adverbs of Frequency (กริยาวิเศษณ์แสดงความถี่) อยู่ในประโยคด้วย
เช่น often, always, sometimes และอื่นๆ ซึ่งมักจะมี Adverb of Time
(กริยาวิเศษณ์แสดงเวลา) ระบุถึงเวลาในอดีตด้วย เช่น last month, last year และอื่นๆ เช่น
I cooked every night last month.
(ฉันทำอาหารทุกคืนเมื่อเดือนที่แล้ว)
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Past Simple Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + Verb2
| ||||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
I / You / We / They | went | to the museum. | ||||||||
| He / She / It | took | a bus to the school. | |||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + did + not + Verb1
| ||||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
I / You / We / They | did | not | go | to the museum. | ||||||
| He / She / It | did | not | take | a bus to the school. | |||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Did + Subject + Verb1?
| ||||||||||
คำถาม
|
Did | I / you / we / they | go | to the museum.? | |||||||
| Did | he / she / it | take | a bus to the school? | ||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + did + Subject +Verb1?
| ||||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
Where
|
did | I / you / we / they | go? | |||||||
How
|
did | he / she / it | go | to the school? | |||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ did not คือ didn’t
2. Past Continuous Tense (อดีตกาลต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +was/were + V -ing
1) ใช้เพื่อกล่าวถึงเหตุการณ์สองเหตุการณ์ที่ เกิดขึ้นซ้อนกันในอดีต โดย…
เหตุการณ์แรกที่เกิดขึ้นและดำเนินอยู่ จะใช้ Past Continuous Tense
เหตุการณ์สั้นๆนั้นได้เข้ามาแทรก จะใช้ Past Simple Tense เช่น
I met you boyfriend in the park while I was jogging.
(ฉันเจอแฟนคุณในสวนตอนฉันกำลังวิ่งจ๊อกกิ้งอยู่)
2) ใช้เพื่อกล่าวถึงเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ เกิดขึ้นในอดีต ในช่วงเวลาที่บ่งไว้อย่างชัดเจน เช่น
I was taking a shower at eight o’clock last night.
(ฉันกำลังอาบน้ำอยู่เมื่อวานตอนสองทุ่ม)
3) ใช้เพื่อกล่าวถึงเหตุการณ์ที่ เกิดขึ้นควบคู่กันไป ณ เวลาเดียวกัน (Parallel Actions) โดย เหตุการณ์ทั้งสองเหตุการณ์จะใช้ Past Continuous Tense เช่น
I was sleeping while the teacher was teaching,
(ฉันนอนหลับขณะที่คุณครูกำลังสอนอยู่)
4) เรามักใช้คำว่า when, while, as ใน Past Continuous Tense เพื่อเชื่อมเหตุการณ์ ต่างๆเข้าด้วยกัน เช่น
As I was going to the church, he was going to the sea.
(ขณะที่ฉันกำลังเดินทางไปที่โบสถ์ เขาก็กำลังไปทะเล)
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Past Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + was/were + V.-ing
| |||||||
บอกเล่า
|
I / He / She / It | was | talking | to her. | ||||
| You / We / They | were | reading | magazines. | |||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + was/were + not + V.-ing
| |||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
I / He / She / It | was | not | talking | to her. | |||
| You / We / They | were | not | reading | magazines. | ||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Was/Were + Subject + V.-ing?
| |||||||
คำถาม
|
Was | I / he / she / it | talking | to her? | ||||
| Were | you / we / they | reading | magazines? | |||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + was/were + Subject + V.-ing?
| |||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
Who
|
was | I / he / she / it | talking to? | ||||
What
|
were | you / we / they | reading? | |||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ was/were not คือ wasn’t และ weren’t
3. Past Perfect Tense
(อดีตกาลสมบูรณ์)
โครงสร้าง : Subject +had + V 3
1)ใช้ กับเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ ที่ เกิดขึ้น และสิ้นสุดลงแล้วในอดีตทั้ง 2 เหตุการณ์ ซึ่งเหตุการณ์หนึ่งได้สิ้นสุดลงก่อนหน้าอีกเหตุการณ์ โดย…
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นและสิ้นสุดลงก่อน จะใช้ Past Perfect Tense
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นและสิ้นสุดลงทีหลัง จะใช้ Past Simple Tense เช่น
We had gone out before he came.
(เราออกไปข้างนอกกันแล้วก่อนที่เขาจะมา)
2) Past Perfect Tense มักจะใช้กับคำว่า before, after, already, just, yet, until, till, as soon as, when, by the time, by… (เช่น by this month) และอื่นๆ โดยจะมีอาจวิธีการใช้ต่างกันไป เช่น
Before + Past Simple Tense + Past Perfect Tense :
Before I went to the school, I had had a car accident.
(ก่อนที่ฉันจะไปโรงเรียน ฉันได้ประสบอุบัติเหตุทางรถยนต์)
After + Past Perfect Tense + Past Simple Tense :
After I had finished my homework, I went to the Internet Café.
(หลังจากที่ฉันทำการบ้านเสร็จ ฉันก็ไปยังร้านอินเตอร์เน็ต)
By he time + Past Simple Tense + Past Perfect Tense :
By the time he came here, I already had finished my dinner.
(ตอนที่เขามาถึง ฉันก็กินข้าวมื้อเย็นของฉันเสร็จเรียบร้อยแล้ว)

วิธีการสร้างประโยค Past Perfect Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + had + Verb 3
| |||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
They | had | gone | to the shopping mall. | ||||||
| She | had | found | her wallet. | |||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + had + not + Verb 3
| |||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
They | had | not | gone | to the shopping mall. | |||||
| She | Had | not | found | her wallet. | ||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Had + Subject + Verb 3?
| |||||||||
คำถาม
|
Had | they | gone | to the shopping mall? | ||||||
| Had | she | found | her wallet? | |||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + had + Verb 3?
| |||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
Where
|
had | they | gone? | ||||||
What
|
had | she | found? | |||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ had not คือ hadn’t
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
(อดีตกาลสมบูรณ์ต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +had+been + V -ing
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +had+been + V -ing
1) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ เกิดขึ้นและดำเนินต่อเนื่องมาจนถึงอีกเหตุการณ์หนึ่งในอดีต โดยอาจใช้กับคำว่า since และ for เช่น
She had been shouting for help since she fell down the stairs.
(เธอได้ร้องขอความช่วยเหลือตั้งแต่เธอได้ตกบันไดลงมา)
2) ใช้พูดถึงการกระทำที่ เกิดขึ้นซ้ำไปซ้ำมาในอดีต และได้สิ้นสุดลงแล้ว เช่น
I had been smoking for 5 months.(ฉันเคยสูบบุหรี่มาเป็นเวลาห้าเดือน)
3) Past Perfect Continuous Tense จะเน้นถึงความต่อเนื่องของการกระทำ (Continuity of action) มากกว่า Past Perfect Tense
That man had been eating pizza when I came in.
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Past Perfect Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + had + been + V.-ing
| |||||||||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
You | had | been | driving | for almost two hours. | |||||||||||
| He | had | been | surfing | the internet since this morning. | ||||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + had + not + been + V.-ing
| |||||||||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
You | had | not | been | driving | for almost two hours. | ||||||||||
| He | had | not | been | surfing | the internet since this morning. | |||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Had + Subject + been + V.-ing?
| |||||||||||||||
คำถาม
|
Had | you | been | driving | for a long time? | |||||||||||
| Had | he | been | surfing | the internet? | ||||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + had + Subject + been + V.-ing?
| |||||||||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
How long
|
had | you | been | driving? | |||||||||||
What
|
had | he | been | doing since this morning? | ||||||||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ had not คือ hadn’t
III.
1. Future Simple Tense (อนาคตกาลปกติ)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject + will + Verb 1
1)
ใช้พูดถึงเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ จะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคต โดยมักใช้กับ Adverb
of Time เช่น tomorrow, next…, soon, shortly, later และอื่นๆ เช่น
I will go to the hospital tomorrow.
(ฉันจะไปโรงพยาบาลในวันพรุ่งนี้)
2) ใช้กับประโยคที่ ตัดสินใจในขณะที่พูด โดยไม่ได้วางแผนมาก่อน เช่น
I think I will buy a new mobile phone next week.
(ฉันคิดว่าฉันจะซื้อมือถือเครื่องใหม่อาทิตย์หน้า)
3) เราอาจใช้ “to be going to” แทน will/shall ใน Future Simple Tense เมื่อ… •กล่าวถึง แผนการ หรือ ความตั้งใจ เช่น
He is going to have a new pet next month.
(เขากำลังจะได้สัตว์เลี้ยงตัวใหม่ในเดือนหน้า)
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Future Simple Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + will/shall + Verb1
| |||||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
They | wil/shalll | go | to the gym tonight. | ||||||||
| She | will/shall | cook | today. | |||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + will/shall + not + Verb1
| |||||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
They | will/shall | not | go | to the gym tonight. | |||||||
| She | will/shall | not | cook | today. | ||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Will/Shall + Subject + Verb1?
| |||||||||||
คำถาม
|
Will/Shall | they | go | to the gym tonight? | ||||||||
| Will/Shall | she | cook | today? | |||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + will/shall + Subject +Verb1?
| |||||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
Where
|
will/shall | they | go | tonight? | |||||||
What
|
will/shall | she | cook | today? | ||||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ will/shall not คือ won’t และ shan’t
2. Future Continuous Tense
(อนาคตกาลต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject +will + be + V-ing
1) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ที่ กำลังจะเกิดขึ้นตามวันหรือเวลาที่กำหนดไว้ในอนาคตอย่างชัดเจน โดยจะสื่อความหมายออกมาว่า เมื่อถึงวันและเวลาที่กำหนดไว้แล้ว เราก็จะเห็นเหตุการณ์นั้นดำเนินอยู่ เช่น
He will be finishing his work at 7 o’clock.
(เขาจะทำงานของเขาเสร็จตอนเจ็ดโมงเช้า)
2) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์หรือการกระทำที่ คาดว่าจะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคตอย่างแน่นอน เช่น
You will be laughing when you see her with that dress.
(คุณจะต้องขำแน่ๆถ้าคุณเห็นเธออยู่ในชุดนั้น)
3) ใช้กับ เหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดไม่พร้อมกันในอนาคต โดย…
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อน จะใช้ Future Continuous Tense
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นหลัง จะใช้ Present Simple Tense เช่น
I will be watching movies when you cook dinner.
(ฉันจะกำลังดูหนังอยู่ในขณะที่คุณทำกับข้าวมื้อเย็น)
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Future Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + will/shall + be + V.-ing
| ||||||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
They | will/shall | be | doing | their homework. | ||||||||
| He | will/shall | be | driving | a car. | |||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + will/shall + not + be + V.-ing
| ||||||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
They | will/shall | not | be | doing | their homework. | |||||||
| He | will/shall | not | be | driving | a car. | ||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Will/Shall + Subject + be + V.-ing?
| ||||||||||||
คำถาม
|
Will/Shall | they | be | doing | their homework? | ||||||||
| Will/Shall | he | be | driving | a car? | |||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + will/shall + Subject + be + V.-ing?
| ||||||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
What
|
will/shall | they | be | doing? | ||||||||
Who
|
will/shall | be | driving? | ||||||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ will/shall not คือ won’t และ shan’t
3. Future Perfect Tense
(อนาคตกาลสมบูรณ์)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject + will + have +V3
ในอนาคต โดยมักใช้กับ by + (by next week, by next month by the end of this year, by 2012, by 6 o’clock, etc.) เช่น
I will have completed my work by tomorrow.
(ฉันจะทำงานของฉันเสร็จสมบูรณ์ในวันพรุ่งนี้)
2) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่คาดเดาว่าจะเกิดขึ้นในอนาคต โดย…
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อน จะใช้ Future Perfect Tense
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นหลัง จะใช้ Present Simple Tense



เช่น The kids will have woken up when we reach home.
(เด็กๆคงจะตื่นกันตอนเรากลับไปถึงบ้าน)
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Future Perfect Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + will/shall + have + Verb 3
| ||||||||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
They | will/shall | have | left | by the time I arrive. | ||||||||||
| He | will/shall | have | finished | his work by 10 o’clock. | |||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + will/shall + not + have + Verb 3
| ||||||||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
They | will/shall | not | have | left | by the time I arrive. | |||||||||
| He | will/shall | not | have | finished | his work by 10 o’clock. | ||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Will + Subject + have + Verb 3?
| ||||||||||||||
คำถาม
|
Will/Shall | they | have | left | by the time I arrive? | ||||||||||
| Will/Shall | he | have | finished | his work by 10 o’clock? | |||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + will + Subject + have + Verb 3?
| ||||||||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
When
|
will/shall
|
they | have | left? | ||||||||||
What
|
will/shall
|
he | have | finished his work? | |||||||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ will/shall not คือ won’t และ shan’t
4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense (อนาคตกาลสมบูรณ์ต่อเนื่อง)
โครงสร้าง :
Subject + will + have +been +V-ing
1) มีวิธีการใช้เหมือนกับ Future Perfect Tense ต่างกันเพียงตรงที่ Future Perfect Continuous Tense นั้น เน้นการกระทำหรือเหตุการณ์ที่ ดำเนินอยู่ ณ เวลาใดเวลาหนึ่งและยังคงจะดำเนินต่อไปอีกในอนาคต โดยมักใช้กับ for + เพื่อแสดงระยะเวลาของเหตุการณ์ หรือ การกระทำนั้นๆ เช่น
By 2012, we will have been living in Bangkok for 7 years.
(ในปี 2012 ก็จะครบรอบที่เราออยู่ในกรุงเทพเป็นเวลา 7 ปีแล้ว)
2) ใช้กับเหตุการณ์ 2 เหตุการณ์ที่ ต้องการเน้นความต่อเนื่องของการกระทำใดการกระทำหนึ่งในอนาคต โดย… เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นก่อน จะใช้ Future Perfect Continuous Tense
เหตุการณ์ที่เกิดขึ้นหลัง จะใช้ Present Simple Tenseเช่น
He shall have been cleaning his room for an hour when I visit him.
(เขาน่าจะกำลังทำความสะอาดห้องของเขาเป็นเวลาหนึ่งชั่วโมงแล้วในตอนที่ฉันไปหาเขา)
วิธีการสร้างประโยค Future Perfect Continuous Tense
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + will + have + been + V.-ing
| |||||||||||||||||||
บอกเล่า
|
You | will/shall | have | been | baking | for one hour by 6 o’clock. | ||||||||||||||
| He | will/shall | have | been | jogging | for two hours by the time I wake up. | |||||||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Subject + will + not + have + been + V.-ing
| |||||||||||||||||||
ปฏิเสธ
|
You | will/ shall | not | have | been | baking | for one hour by 6 o’clock. | |||||||||||||
| He | will/ shall | not | have | been | jogging | for two hours by the time I wake up. | ||||||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Will + Subject + have + been + V.-ing?
| |||||||||||||||||||
คำถาม
|
Will/shall | you | have | been | baking | by 6 o’clock? | ||||||||||||||
| Will/shall | he | have | been | jogging | by the time I wake up? | |||||||||||||||
โครงสร้าง
|
Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + will + Subject + have + been + V.-ing?
| |||||||||||||||||||
คำถาม
Wh- |
How long
|
will/shall | you | have | been | baking by 6 o’clock? | ||||||||||||||
What
|
will/shall | he | have | been | doing by the time I wake up? | |||||||||||||||
*คำปฏิเสธรูปย่อของ will/shall not คือ won’t และ shan’t
ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น